|
 |
1. The word "energy" has two parts --
the Greek words 'en' and 'ergon'.
What do the Greek words mean?
Explain why they were chosen to form the word energy.
2. What is one thing in your every day life that would change dramatically without energy?
3. How does the U.S. compare with other countries as far as our usage of wind energy?
4. What is the government doing to try to encourage the use of wind energy?
|
|

Renewable and Nonrenewable Energy
As you investigate renewable and nonrenewable energy, make sure you can:
- Explain why the world is beginning to experiment with alternative energy sources.
- List types of renewable energy and explain the advantages and disadvantages of each.
- List types of nonrenewable energy sources and explain the advantages and disadvantages of each.
|
|
Renewable energy sources can be replenished in a short period of time.
Read about Renewable Energy Sources and answer the questions.
1. The video explained how geothermal energy -- a renewable energy source -- works.
What is another renewable energy source?
2. How does using renewable energy help the environment? the economy?
Energy sources that cannot be replenished in a short period of time.
Read about Nonrenewable Energy Sources and answer the questions.
3. Nonrenewable energy comes from fossil fuels. Explain what that means.
4. How does using nonrenewable energy help the environment? the economy?
|

Motion - Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is energy of motion and movement. Investigate this section and learn how motion can be used as an energy source. Objects and substances move when a force is applied according to Newton's Laws of Motion.
|
Newton's Laws of Motion
Motion to Energy Website

|
M2E Power
Idaho National Labs Intro
Motion to Energy Website


|
Idaho Green Living
Turning Motion Into Power
Motion to Energy Website


|
|
 |
| 1. Explain one discovery that Isaac Newton made about motion.
2. Give an example of how motion can be turned into energy.
3. Why is M2E considered “green” energy?
|
|

Thermal Energy
Which atoms move more quickly- atoms that are cool or warm ones? I hope you said warm ones. That increased movement results in an increase in temperature. Investigate this section and see how heat can be used to create energy.
|
Energy Story - Geothermal 1


Energy Story - Geothermal 2


from The Energy Story |
Solar Thermal Energy


Ocean Thermal Energy


|
Geothermal Energy
Yellowstone National Park


How
A Geothermal Plant Works


|
|
 |
| 1. Not every area is suitable for geothermal energy. What must be in place in order to produce power using geothermal energy?
2. Denmark has relied on wind energy for years, but has found, in some areas, a different way to get their hot water. Explain how this works.
3. California has many areas that could one day generate power using geothermal energy. Give 3 ways this would help the residents of California, as well as the rest of the country.
|
|

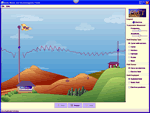
Electricity
STOP! Before you plug in that radio, do you know how that energy got to your house? Investigate this section to find out and to learn why that doorknob shocks you when you touch it.
|
Nikola Tesla


"Tesla is often described as the most important scientist and inventor of the modern age... He is best known for many revolutionary contributions in the field of electricity and magnetism in the late 19th and early 20th centuries." Wikipedia |
School House Rock


Electric Circuit

|
Introduction


Electricity & Circuits

 |
Potato Experiment


Generators


From The Energy Story
|
|
 |
1. Explain in your own words how electricity is generated.
Try to use words such as electrons, magnet, generator, current, etc.
2. Series and Parallel are two types of circuits.
Why would you want your home wired with parallel circuits and not series circuits?
|
|

Radiant Energy
Radiant is the energy of electromagnetic waves. Examples include: radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation,
X-rays and gamma rays. Solar energy is an example of radiant energy.
My dog’s favorite place to lie is under a window on a sunny day. The bright rays heat up the room and keep her comfortable. That is radiant heat. Remember how you get close to the fire in the winter so that you can warm your hands and face? That also is radiant energy, and all that energy becomes thermal energy as it warms us. Investigate this section and learn how the sun’s radiant energy can be used to create energy
You can learn more about radiant heating at this website from the U.S. Department of Energy - A Consumer's Guide to Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy - Radiant Heat .
|
| X-Rays


Invisible, highly penetrating electromagnetic radiation of a much shorter wavelength than visible light, discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm C. Roentgen. |
Radio Waves

|
Energy Story - Solar

 Part 1 Part 1
 Part 2 Part 2
 Part 3 Part 3
|
|
 |
1. Who would have ever thought that tape cold be used to make X-rays?
How would this be helpful to undeveloped countries?
2. Our calculators work using solar energy.
Name 3 other ways that solar energy can be used.
3. If a community depended on solar energy to make electricity, they would have to have an alternate plan for nighttime and cloudy days. What do they do to ensure there is no interruption of service?
|
|

Sound Energy
"Sound is a vibration. When something makes a noise it is vibrating, and this causes air molecules around it to vibrate too. These vibrations are transmitted through the air, to our ears, where we perceive them as sound." You'll find out more about sound, learn how to perform a simple sound experiment, and find out about the loudest animal on earth at the Sound Web Page.
|
Sound is Energy


|
Sound Waves


|
Sound & Solids


|
|
 |
1. How does increasing or decreasing the amplitude affect the sound?
2. How does increasing or decreasing the frequency affect the sound?
3. Does sound travel better through air or a solid? Explain how you could prove your answer.
|
|
|

|
 |
1. Many people assume that hydrogen cars would not pollute the environment.
Explain why this is not entirely true.
2. Chemical energy is passed from one organism to another in a coral reef.
Why could we say that all of these organisms depend on the sun?
3. Gasoline, hydrogen and coal are all chemicals that provide energy.
What is providing the energy in the bottle rocket?
|
|

|
 |
| 1. What are 3 advantages to using nuclear power?
2. What are 3 disadvantages to using nuclear energy?
3. How does the energy output from coal differ from the energy output from uranium?
|
|
|
CLICK AND
SCROLL TO
BOTTOM
TO
SHOW & PRINT YOUR WORK
DIRECTIONS
Click on the yellow arrows starting with the Energy Overview Section. Click the arrow again to close a section.
ENERGY WEBSITE LINKS
Challenge:
How to Make a Windmill
* On YouTube
Overview:
Multimedia Biographies
Solar:
Nuclear:
Geothermal:
Fossil Fuels:
Hydroelectric Power:
Wind Energy:
Tidal Energy:
Energy from Biomass:
|
|